使用Moveit2
一、为URDF添加碰撞描述
拥有碰撞体积,才能更好的计算机械臂的运动轨迹,防止机械臂发生一些意想不到的问题。下面为机械臂添加碰撞体积,只需要修改arm.xacro这个文件:
以base_link为例,现在是没有碰撞体积的:
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.4 0.4 0.1"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.05" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0"/>
<material name="grey" />
</visual>
</link>添加碰撞体积,只需要在link组件里加上collosion标签,collosion标签和视觉标签里的内容一致,这样显示的就是真正的碰撞体积。(如果零件复杂,也可以简化碰撞体积的结构,可以让计算更简单)
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.4 0.4 0.1"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.05" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0"/>
<material name="grey" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="0.4 0.4 0.1"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.05" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0"/>
</collision>
</link>只需要给所以有实体的link 加上collosion标签。
这里代码太长,就不贴了,在本节后面的链接里自行寻找。
最后在可视化工具里显示碰撞体积如下:
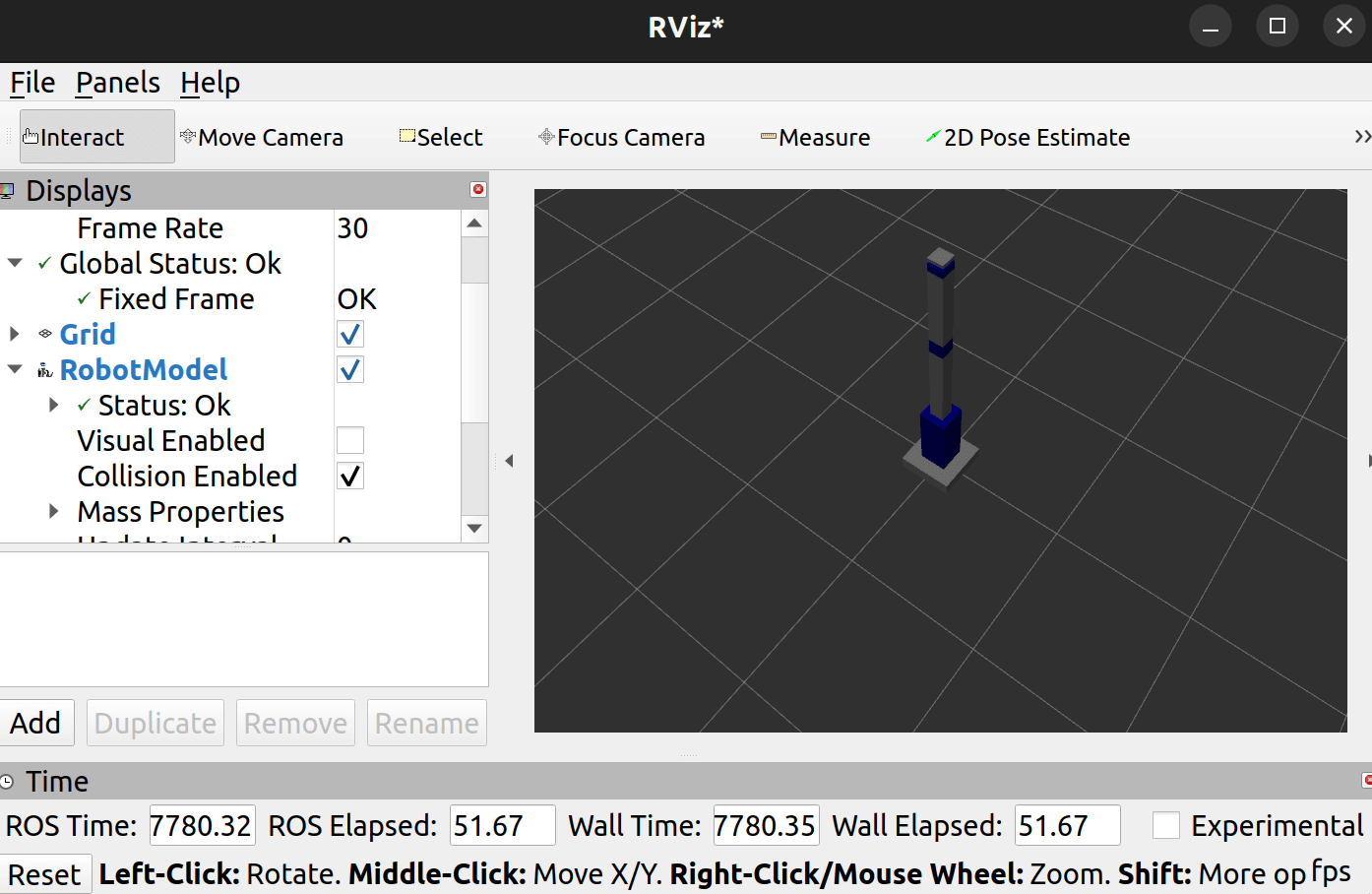
代码: https://github.com/DuRuofu/moveit2_learn/commit/459522fd2d176579e48db462ebc34c5e7694e826
二、配置Moveit2
2.1 启动配置助手
我们启动Moveit2 配置助手:
安装:
sudo apt install ros-humble-moveit-setup-assistant启动(在工作区目录下启动,否则下一步选择urdf文件会闪退):
ros2 launch moveit_setup_assistant setup_assistant.launch.py启动后如下:
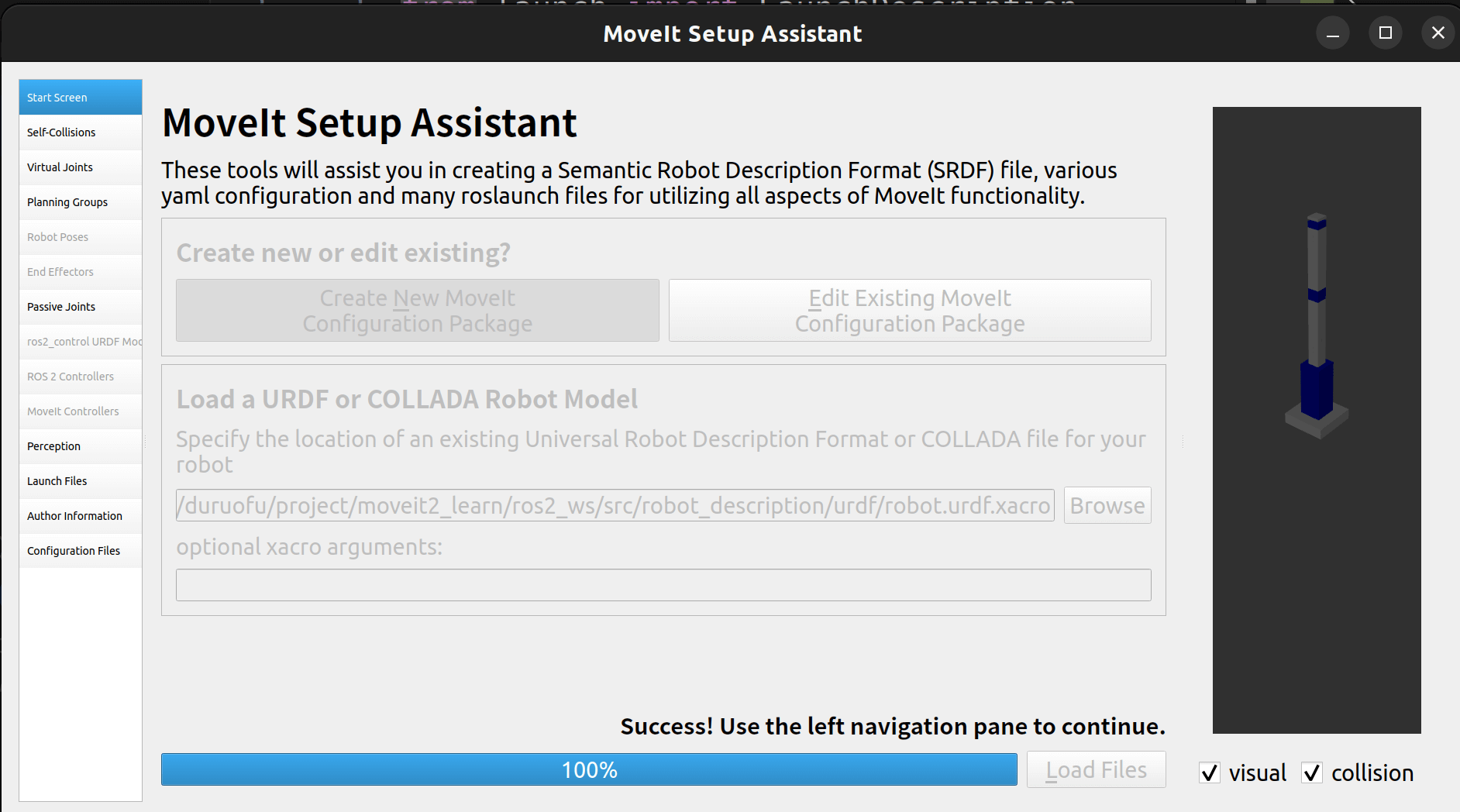
2.2 加载URDF文件
选择创建新的配置包,然后选择我们的urdf文件,这里可能会闪退,可以看文后参考文献第一条。
选择URDF文件后,点击加载,如下:
2.3 自碰撞检测
点击Generate Collision Matrix自动生成即可: 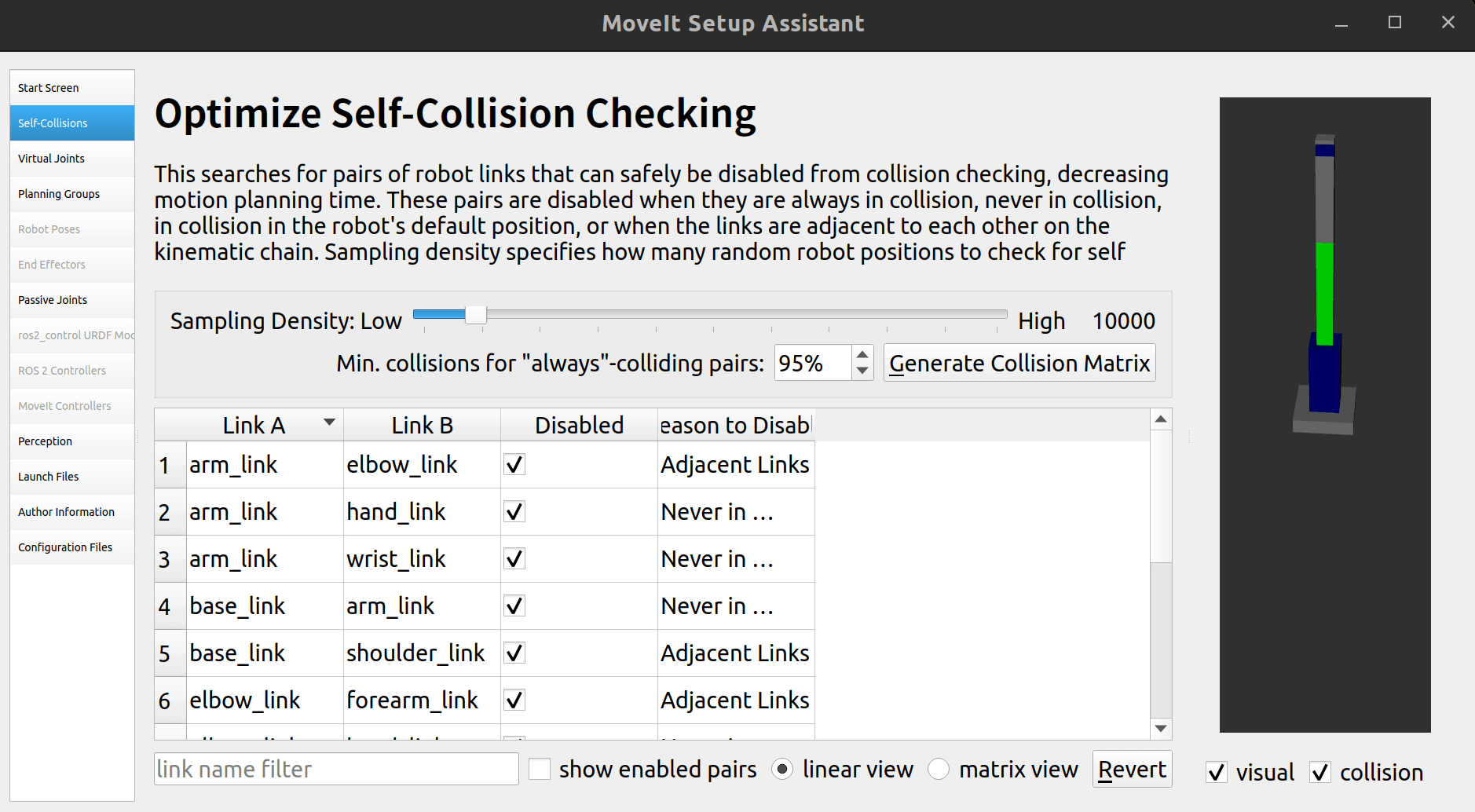
2.4 虚拟关节
这里建立一个虚拟关节,用于将机器让的base_link和世界坐标系联系起来。 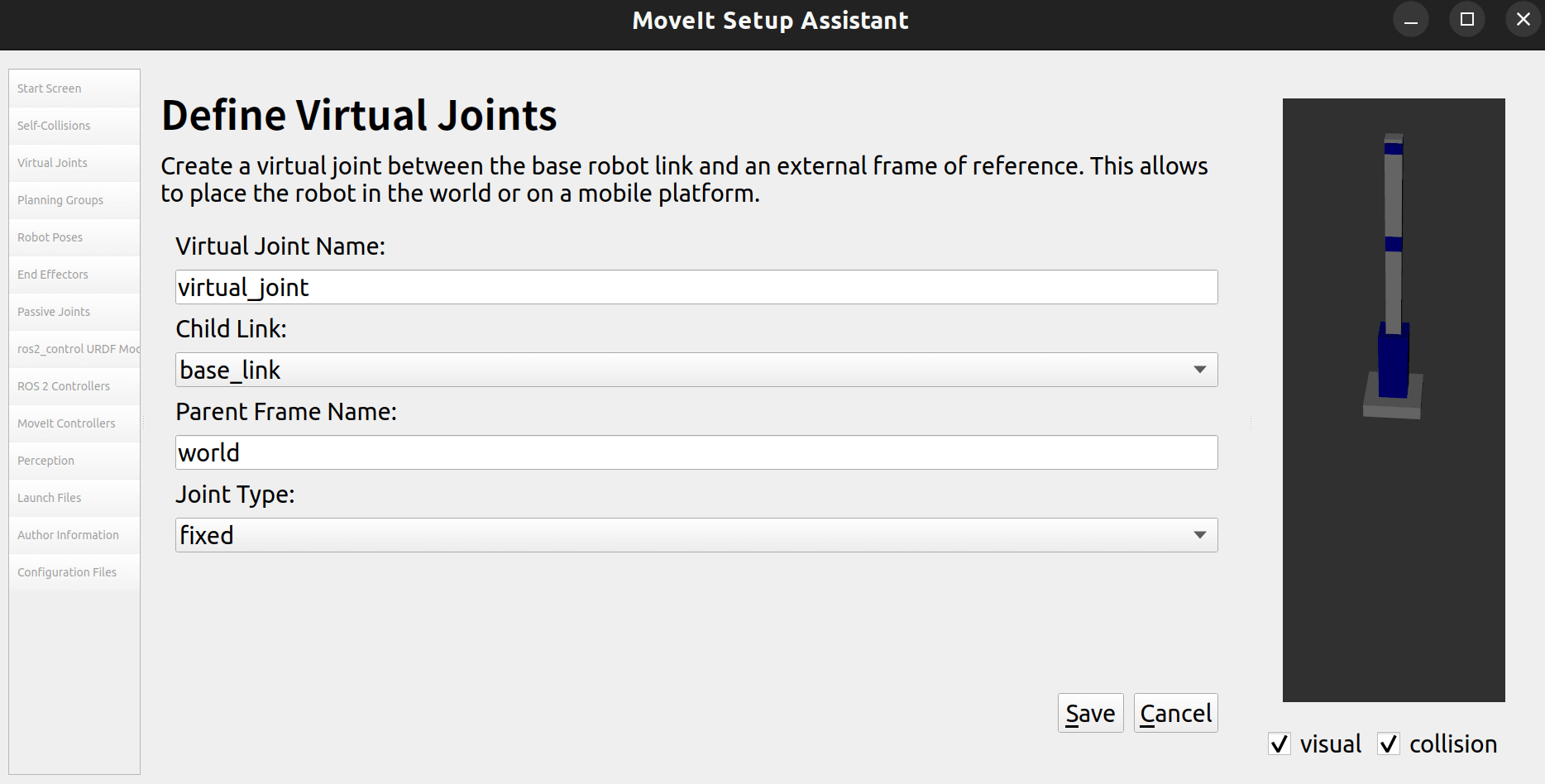
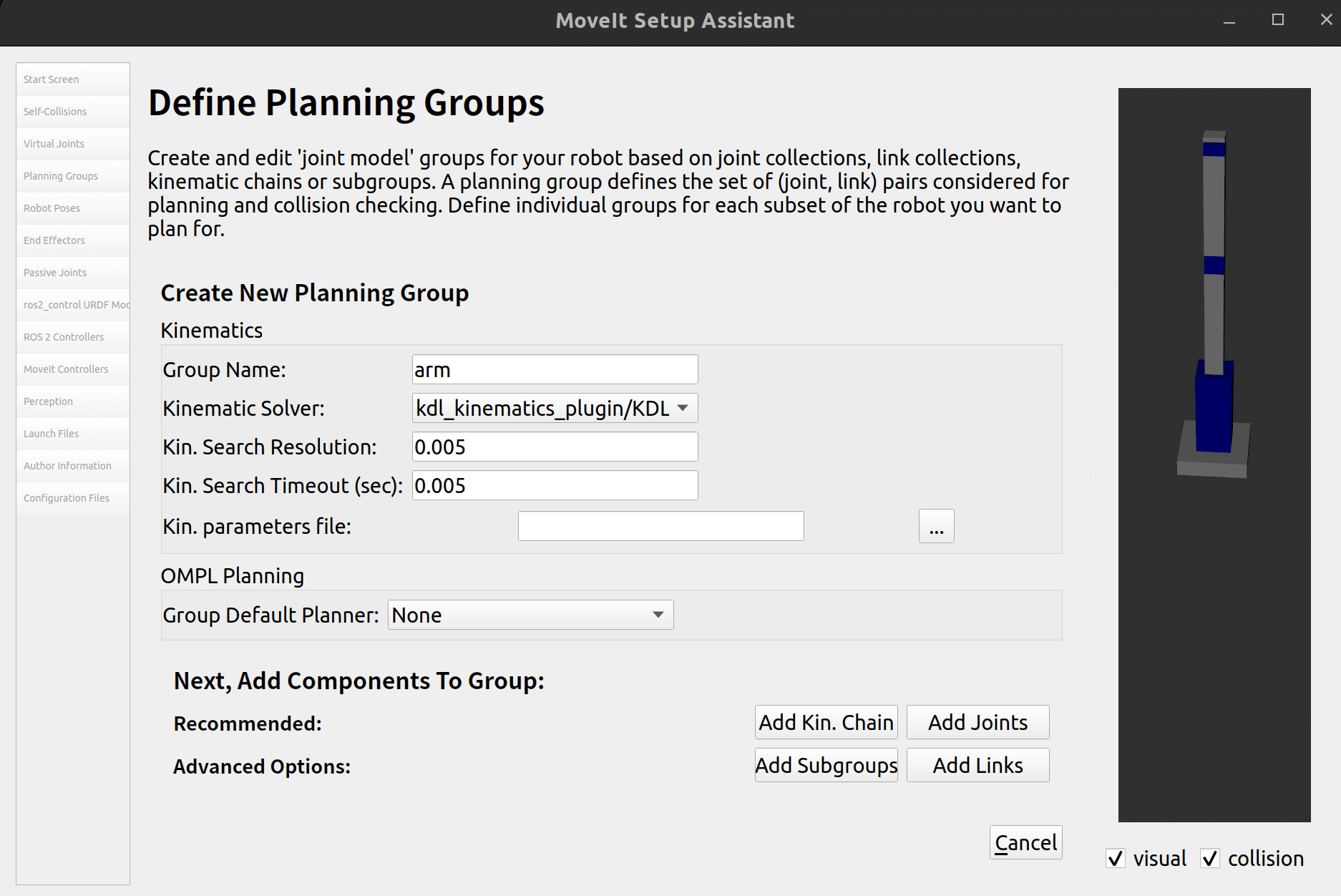
2.5 规划组
添加一个规划组:
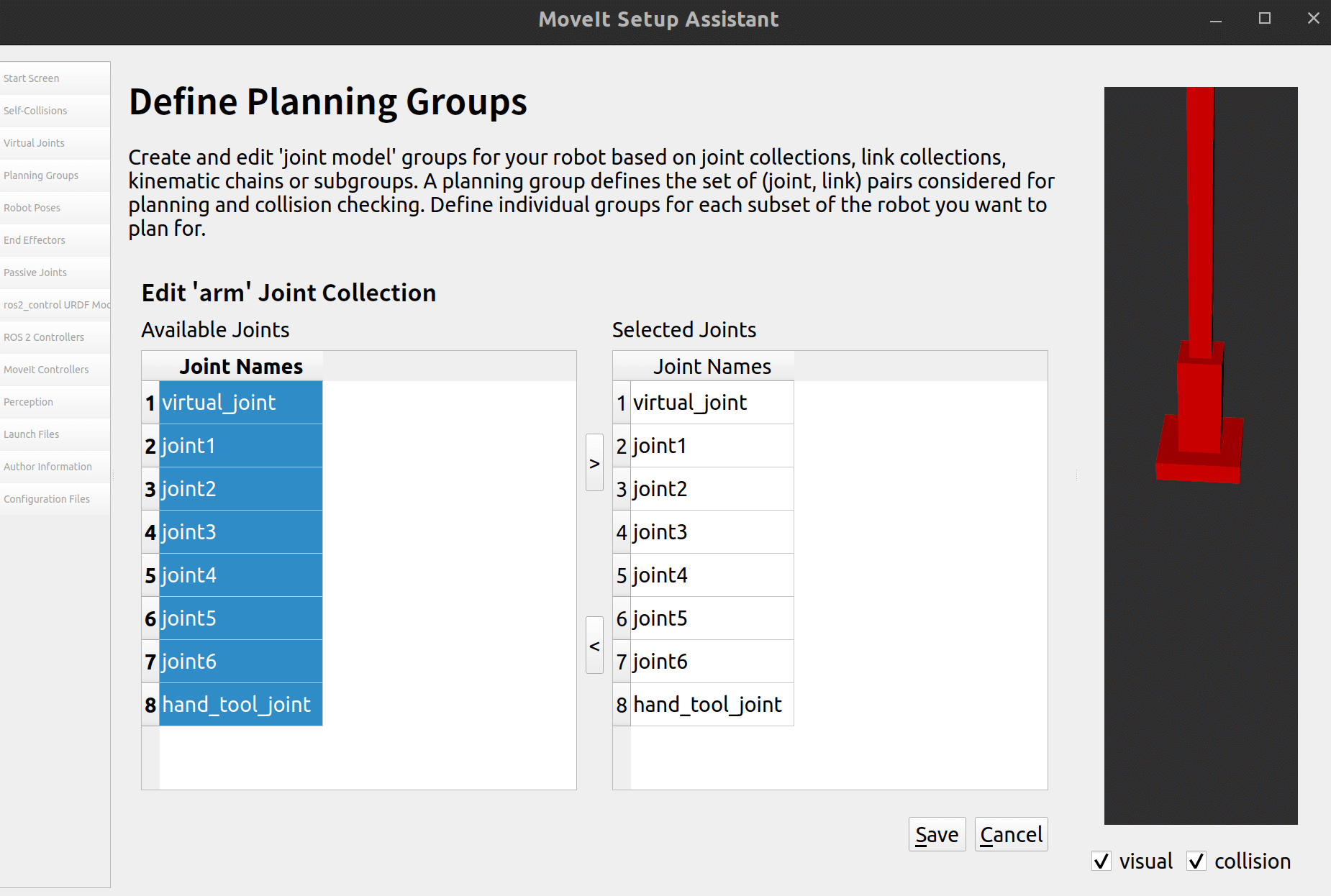
点击添加关节,全部添加:
保存,最终如下: 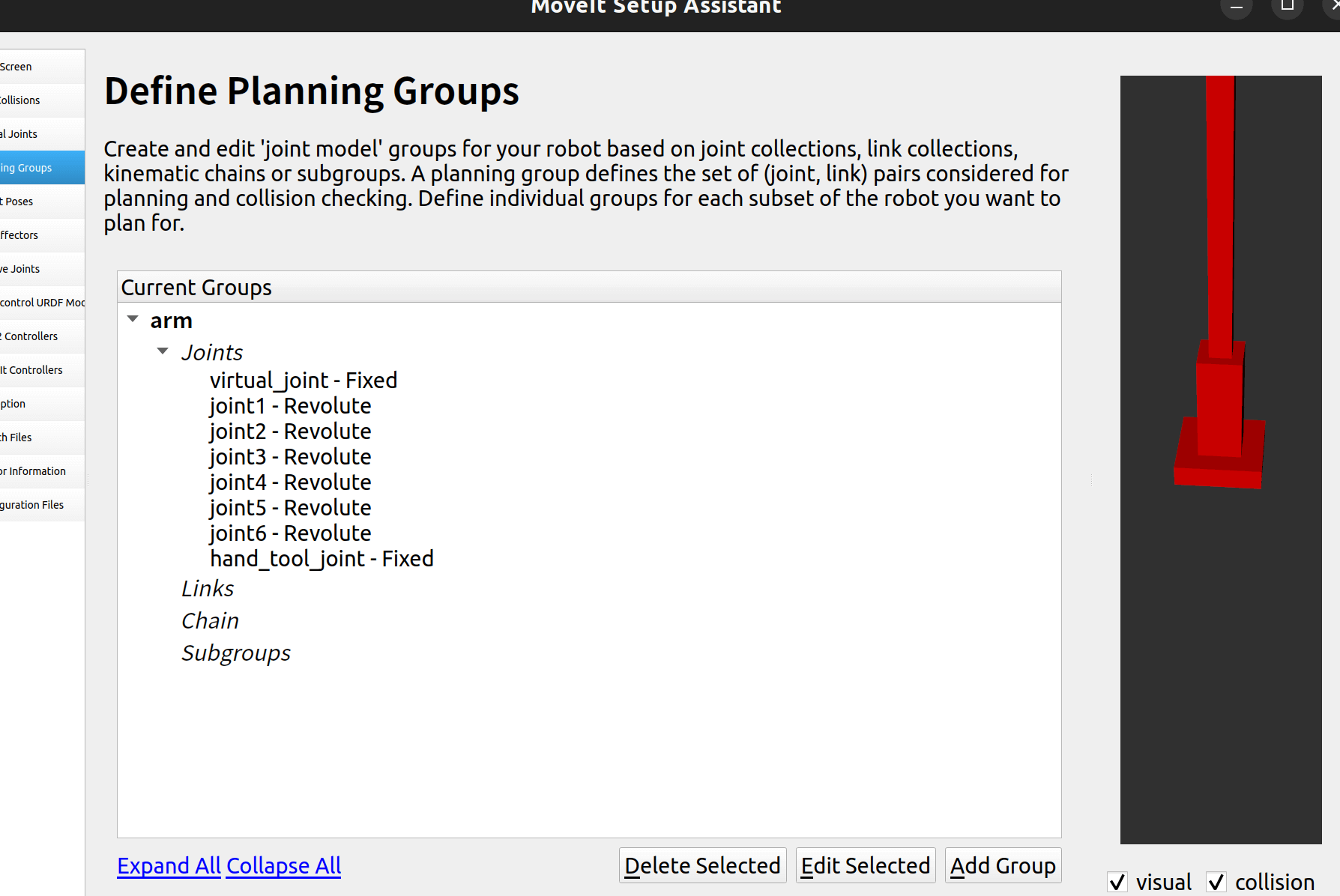
2.6 定义机器人姿态
我们可以预先定义几个姿态,便于测试 和机械臂在不同姿态间转换。
定义初始姿态:
2.7 定义末端执行器
这里先不添加
2.8 定义被动关节
这里也是无 
2.9 定义ros2_control控制器
这样使用位置控制和位置反馈 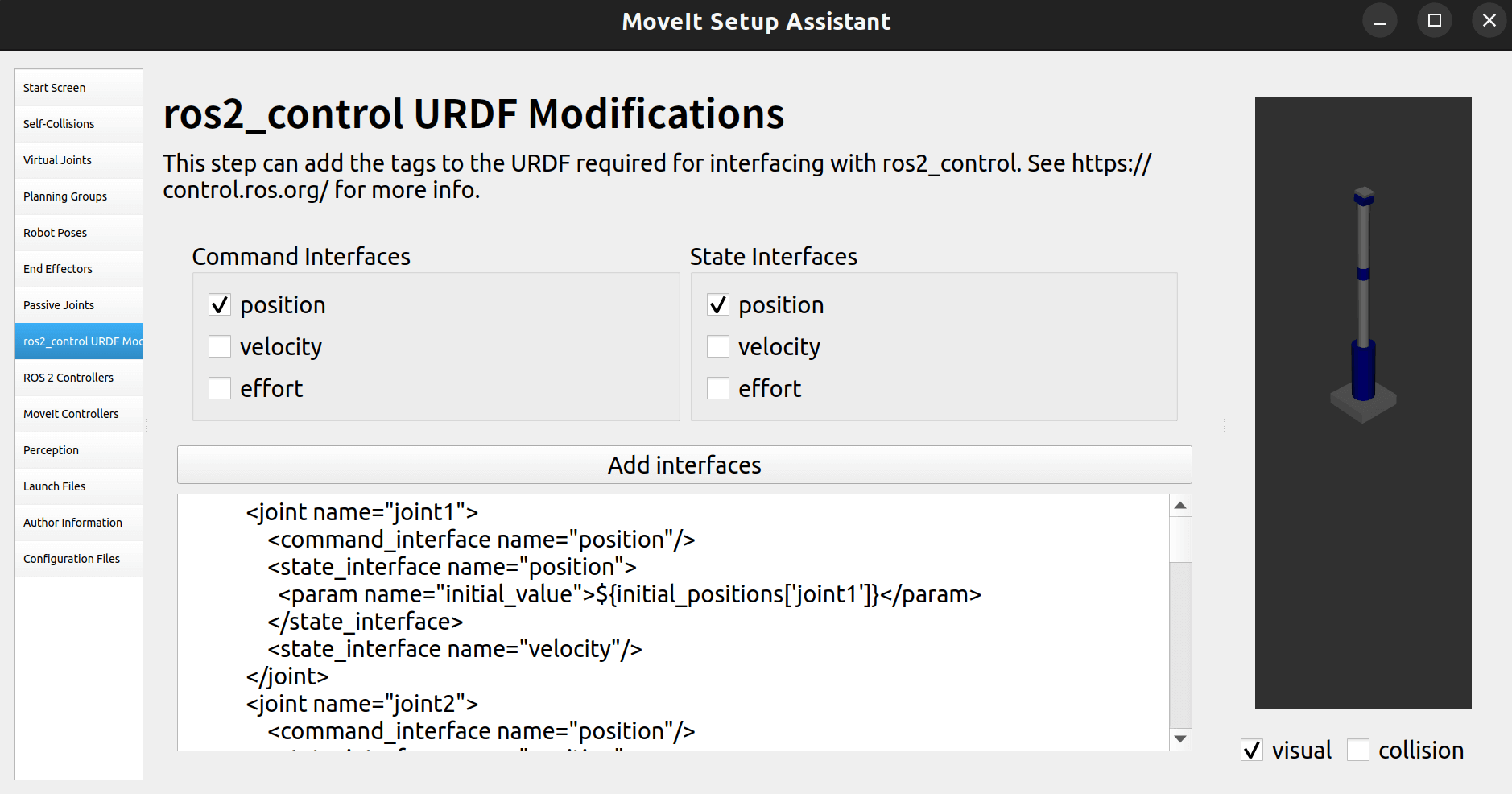
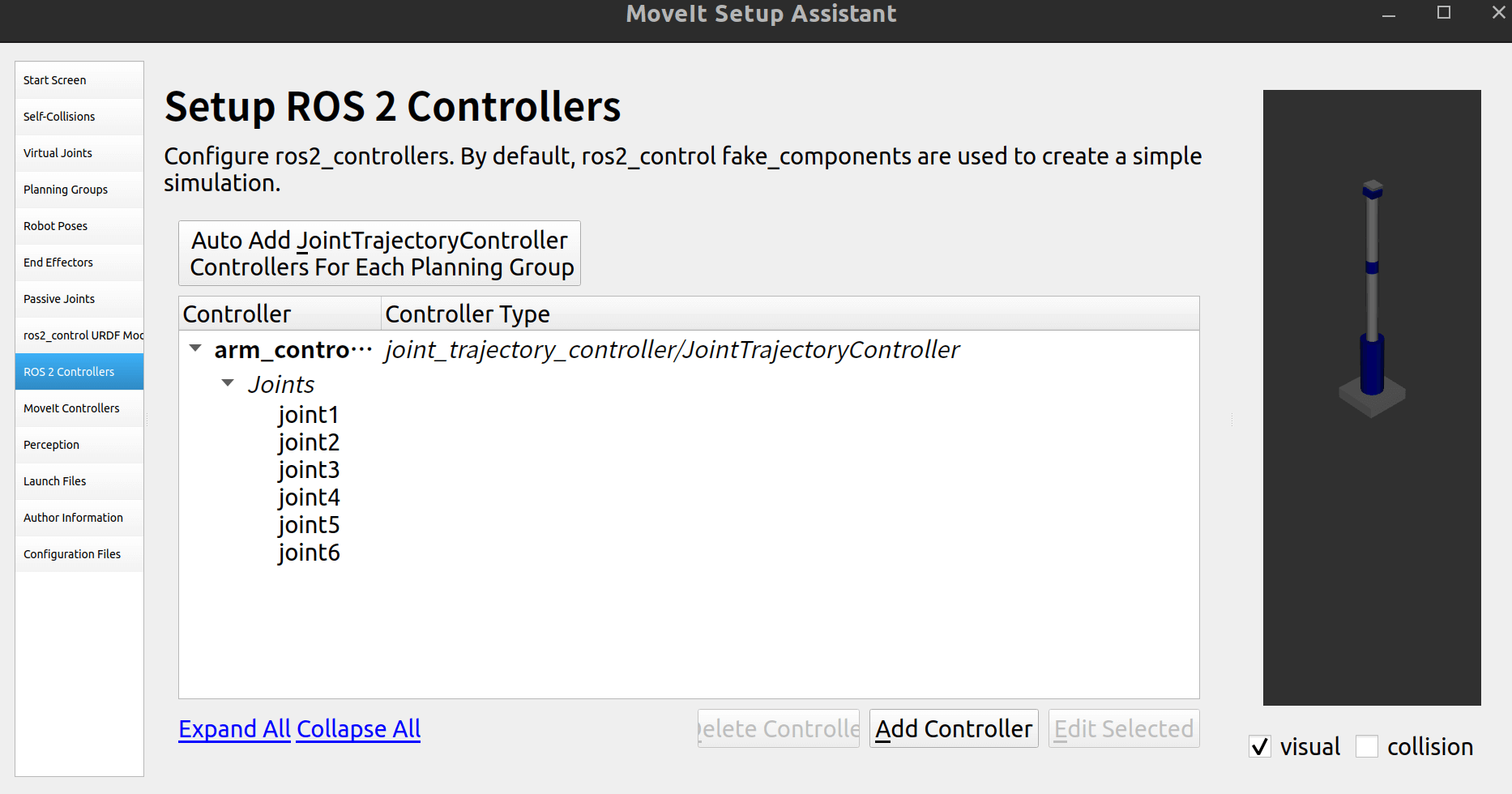
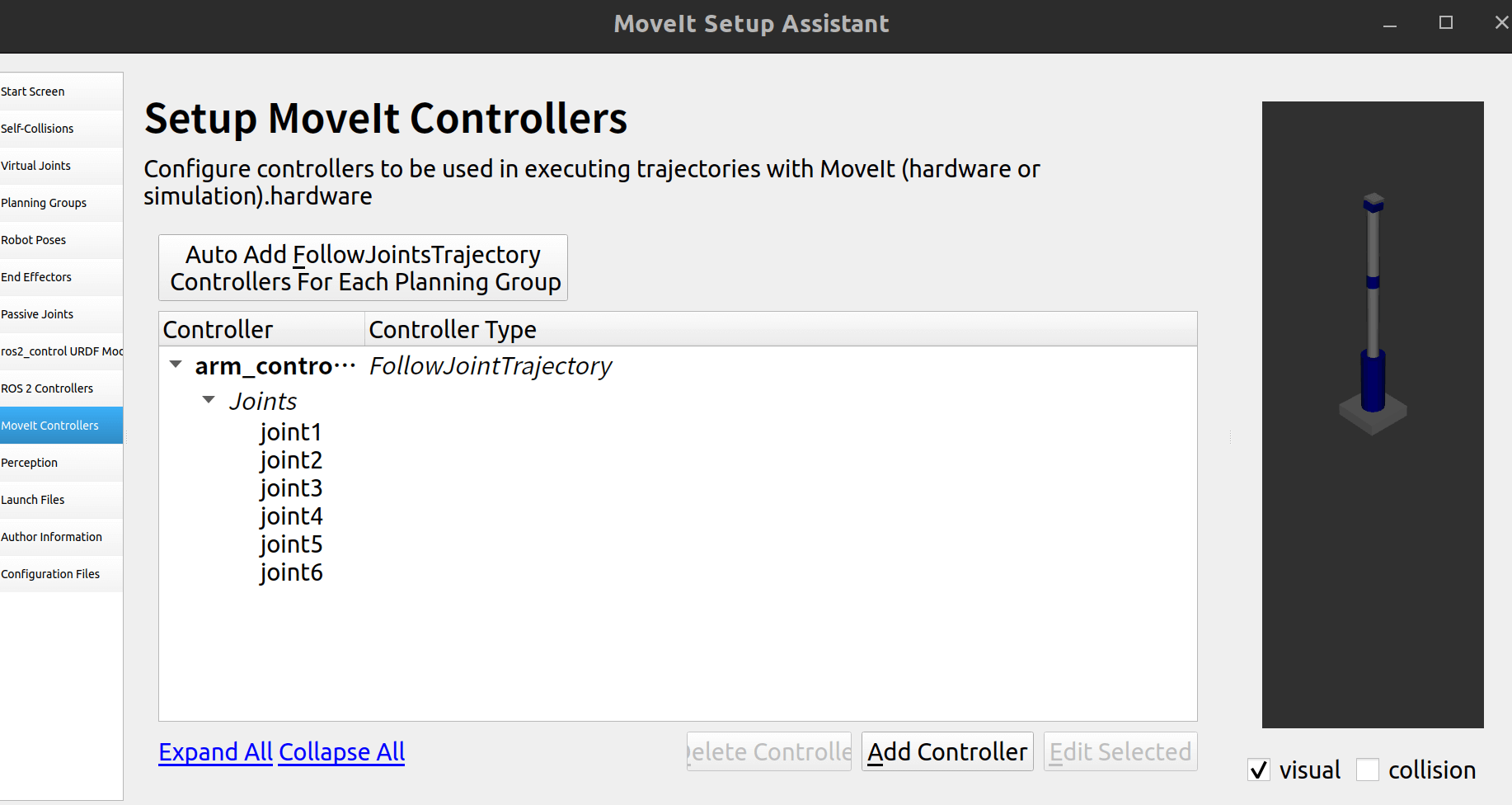
2.10 控制器配置
自动创建:
2.11 传感器配置
无
2.12 启动文件配置
默认
2.13 作者信息
不要留空,不然会报错 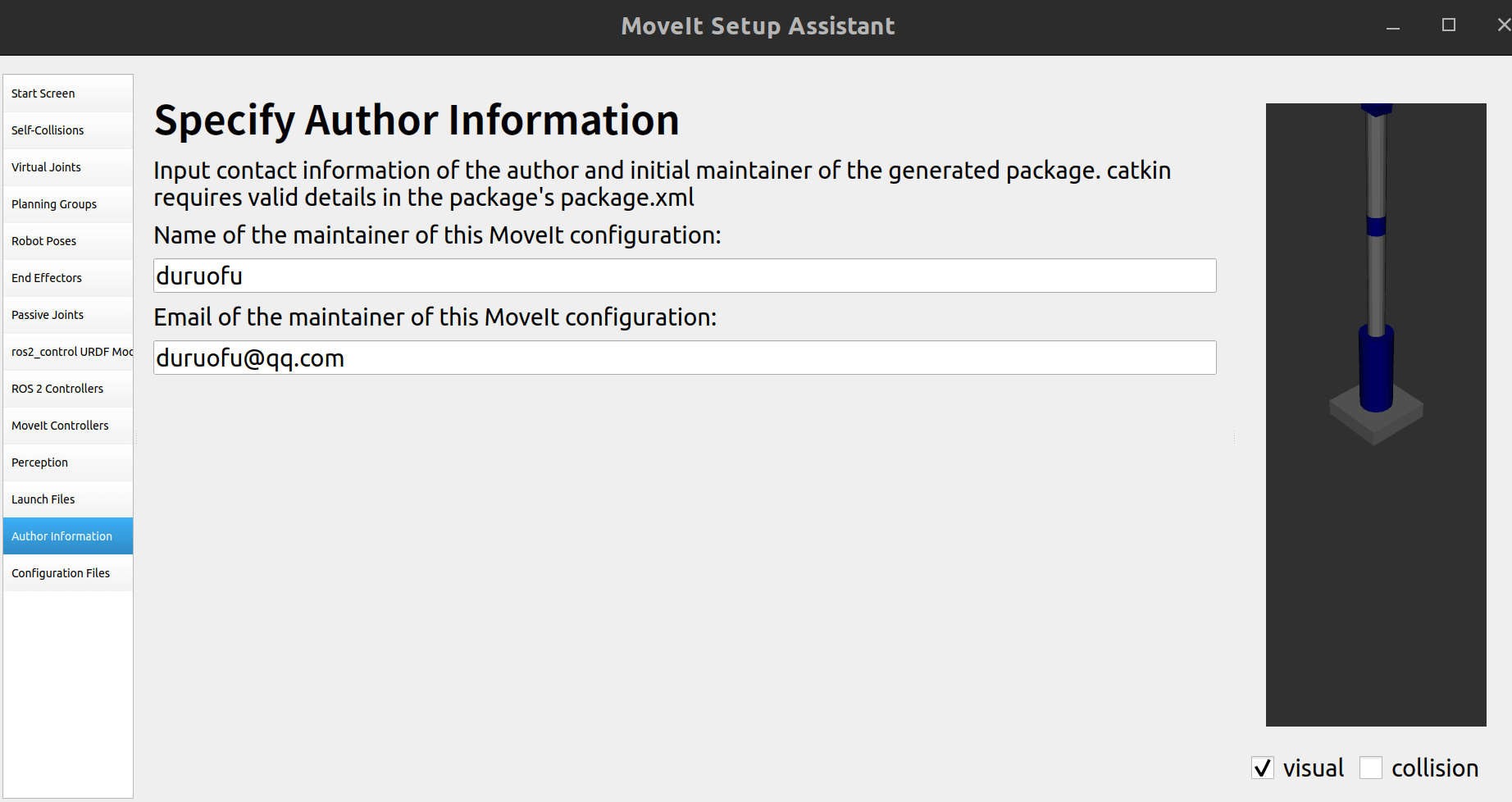
2.14 配置文件
填写包存放的目录,这里新建一个包my_robot_moveit_config
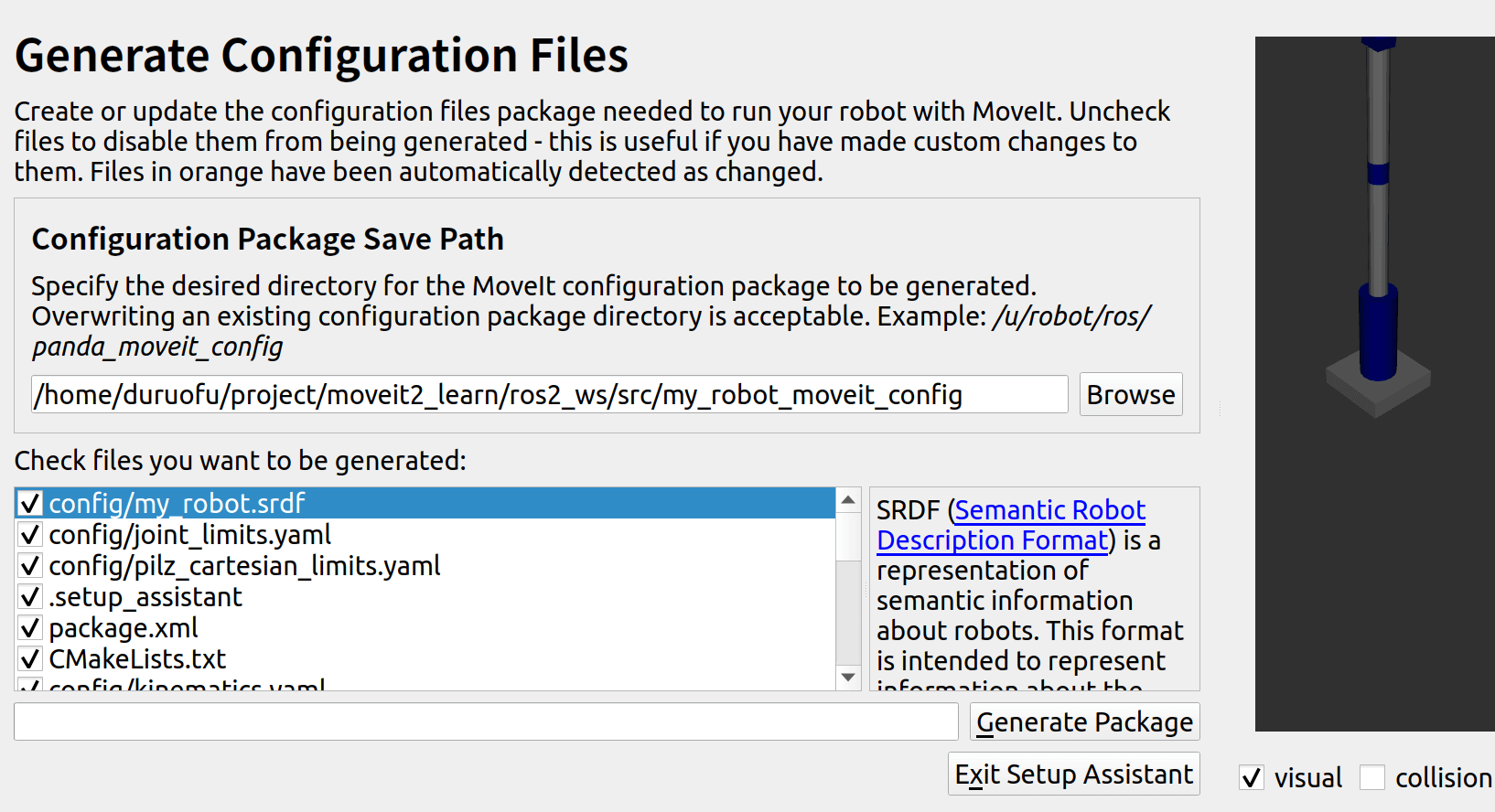
点击创建包即可:
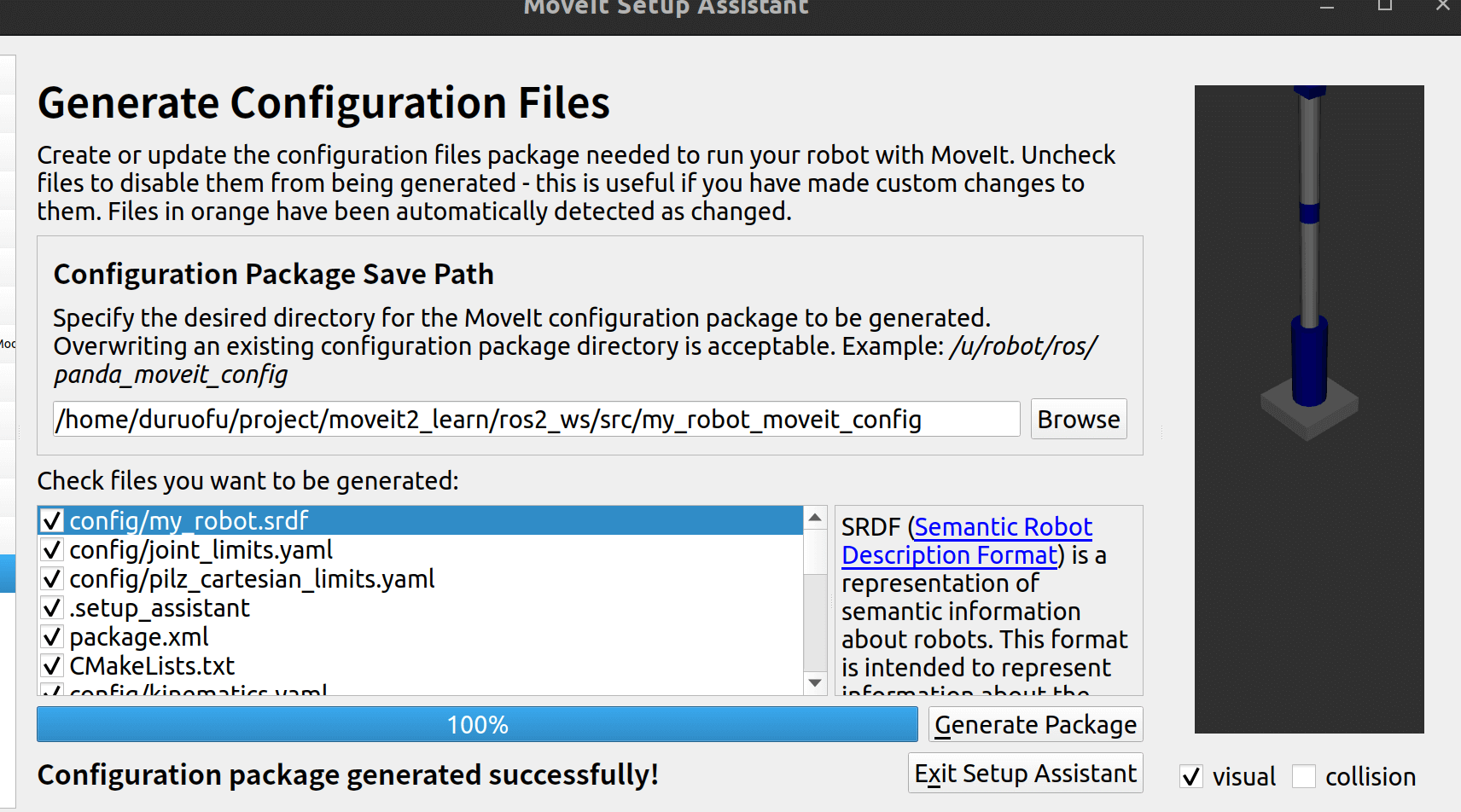
创建成功,工作区里也生成了新的包:
关于这些文件各自的作用,可以参考:ros2控制六轴机械臂教程 ,这里不在赘述
代码: https://github.com/DuRuofu/moveit2_learn/commit/66c46529412852670001891ff9782085d9d3bc1d
三、测试Moveit2配置包
cd ros2_ws
colcon build
source install/setup.bash
ros2 launch my_robot_moveit_config demo.launch.py这里可能会报错,找不到controller_manager 和其他包,安装一下:
sudo apt install ros-humble-controller-manager
sudo apt install ros-humble-joint-trajectory-controller
sudo apt install ros-humble-joint-state-broadcaster
sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-moveit-planners-ompl
sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-moveit-planners-chomp
sudo apt-get install ros-humble-moveit-ros-control-interface
sudo apt-get install ros-humble-ros2-control再次运行还会遇到其他报错,这里我们还要修改joint_limits.yaml文件:
# joint_limits.yaml allows the dynamics properties specified in the URDF to be overwritten or augmented as needed
# For beginners, we downscale velocity and acceleration limits.
# You can always specify higher scaling factors (<= 1.0) in your motion requests. # Increase the values below to 1.0 to always move at maximum speed.
default_velocity_scaling_factor: 0.1
default_acceleration_scaling_factor: 0.1
# Specific joint properties can be changed with the keys [max_position, min_position, max_velocity, max_acceleration]
# Joint limits can be turned off with [has_velocity_limits, has_acceleration_limits]
joint_limits:
joint1:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0
joint2:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0
joint3:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0
joint4:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0
joint5:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0
joint6:
has_velocity_limits: true
max_velocity: 1.0
has_acceleration_limits: true
max_acceleration: 1.0再次运行显示如下:
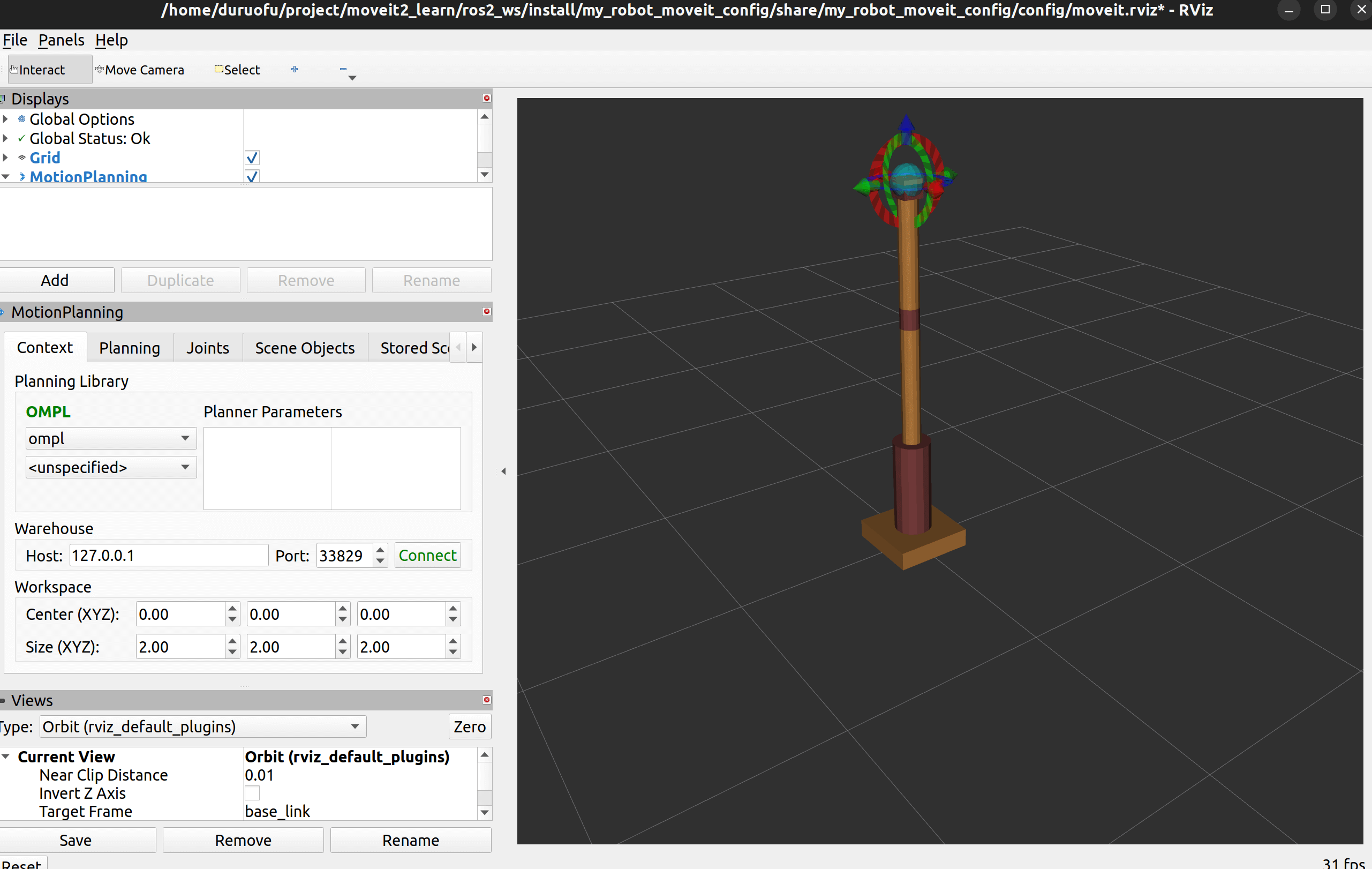
可以在规划页面选择起始和终止姿势,进行轨迹规划:
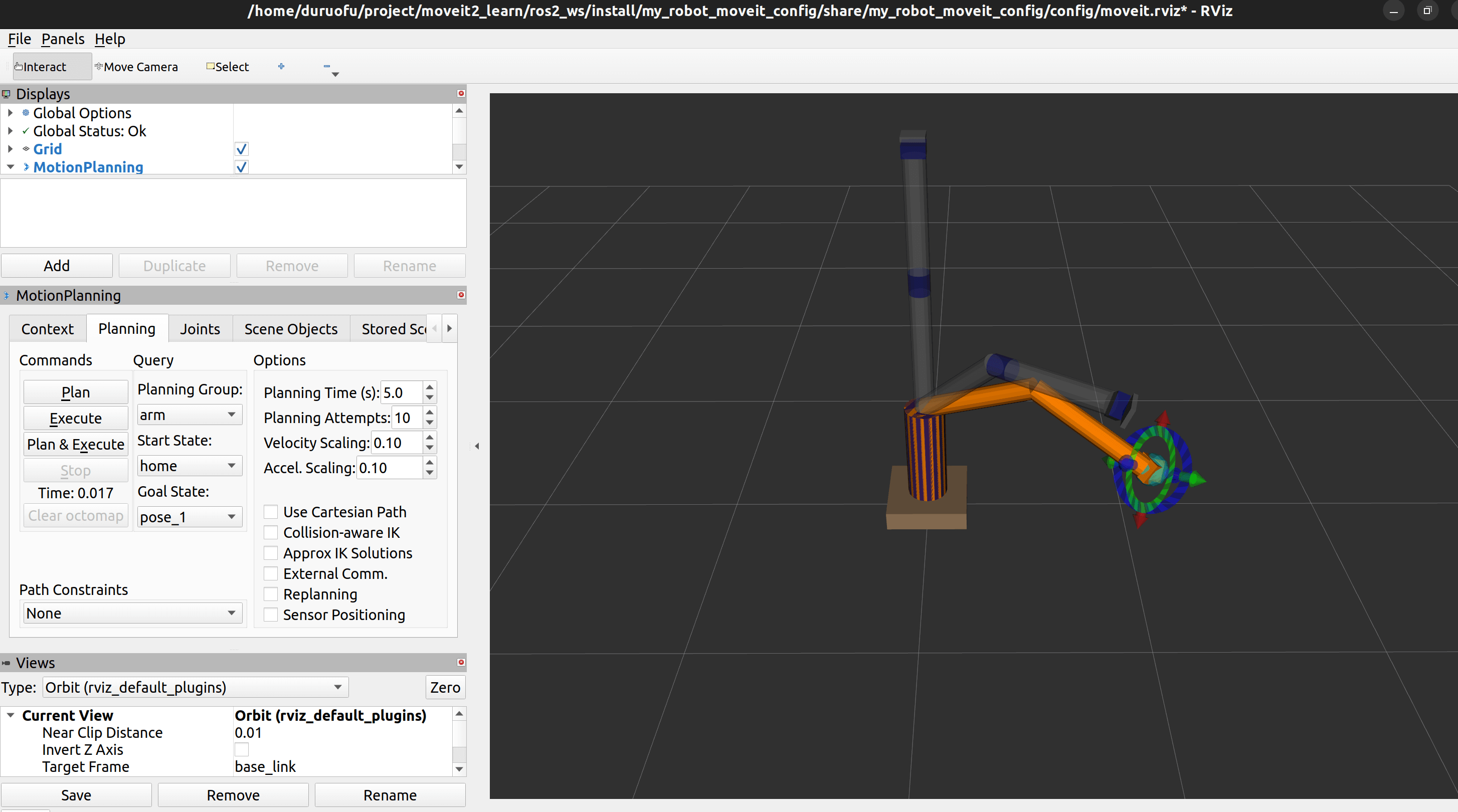
这里moveit_controllers.yaml也要修改,如下
# MoveIt uses this configuration for controller management
moveit_controller_manager: moveit_simple_controller_manager/MoveItSimpleControllerManager
moveit_simple_controller_manager:
controller_names:
- arm_controller
arm_controller:
type: FollowJointTrajectory
joints:
- joint1
- joint2
- joint3
- joint4
- joint5
- joint6
action_ns: follow_joint_trajectory
default: true这样就可以在Planning页面,实际执行规划动作。至此我们完成了Moveit的基本使用。
代码: https://github.com/DuRuofu/moveit2_learn/commit/4ea962398e99c52964aa172db74cc5b068bc4ca4
